Deploy Imposter to AWS Lambda using the AWS Console
This section describes how to deploy Imposter as an AWS Lambda function using the AWS Console.
Other ways to deploy to Lambda
You can also deploy Imposter as a Lambda function using the Imposter CLI, infrastructure as code tools (e.g. Terraform) or a framework such as Serverless.
Overview
The key steps are:
- you upload the Imposter ZIP file and your configuration files to an S3 bucket
- you create a Lambda function using the ZIP file as the code source
- you set the environment variables of the function to refer to the configuration path in S3
- you access the Lambda function via a Lambda Function URL or Amazon API Gateway
Prerequisites
You must have an AWS account and permission to deploy Lambda functions, create/write to an S3 bucket, and configure API Gateway.
Upload configuration to S3 bucket
We are going to store the Imposter configuration files in an S3 bucket. Upload your configuration files to the S3 bucket, under a path such as config.
For the purposes of this guide, we will assume you have uploaded the configuration to a bucket named example-imposter-bucket, so the full path to the configuration file would be:
You may add related files here, such as response files, specifications etc.
s3://example-imposter-bucket/config/openapi-spec.yaml
s3://example-imposter-bucket/config/response.json
...
Deployment steps
This method uses the AWS Web Console to create a Lambda function, and enables you to call it using the Lambda Function URL.
Step 1: Upload Imposter to an S3 bucket
The Imposter engine for AWS Lambda is packaged as a ZIP file. You should upload this file to an S3 bucket, from where it will be referenced by your Lambda function.
Open the AWS S3 Console. Upload the imposter-awslambda.zip file from the Releases page to an S3 bucket.
For the purposes of this guide, we will assume you have uploaded the ZIP file to a bucket named example-imposter-bucket, so the full path to the file would be:
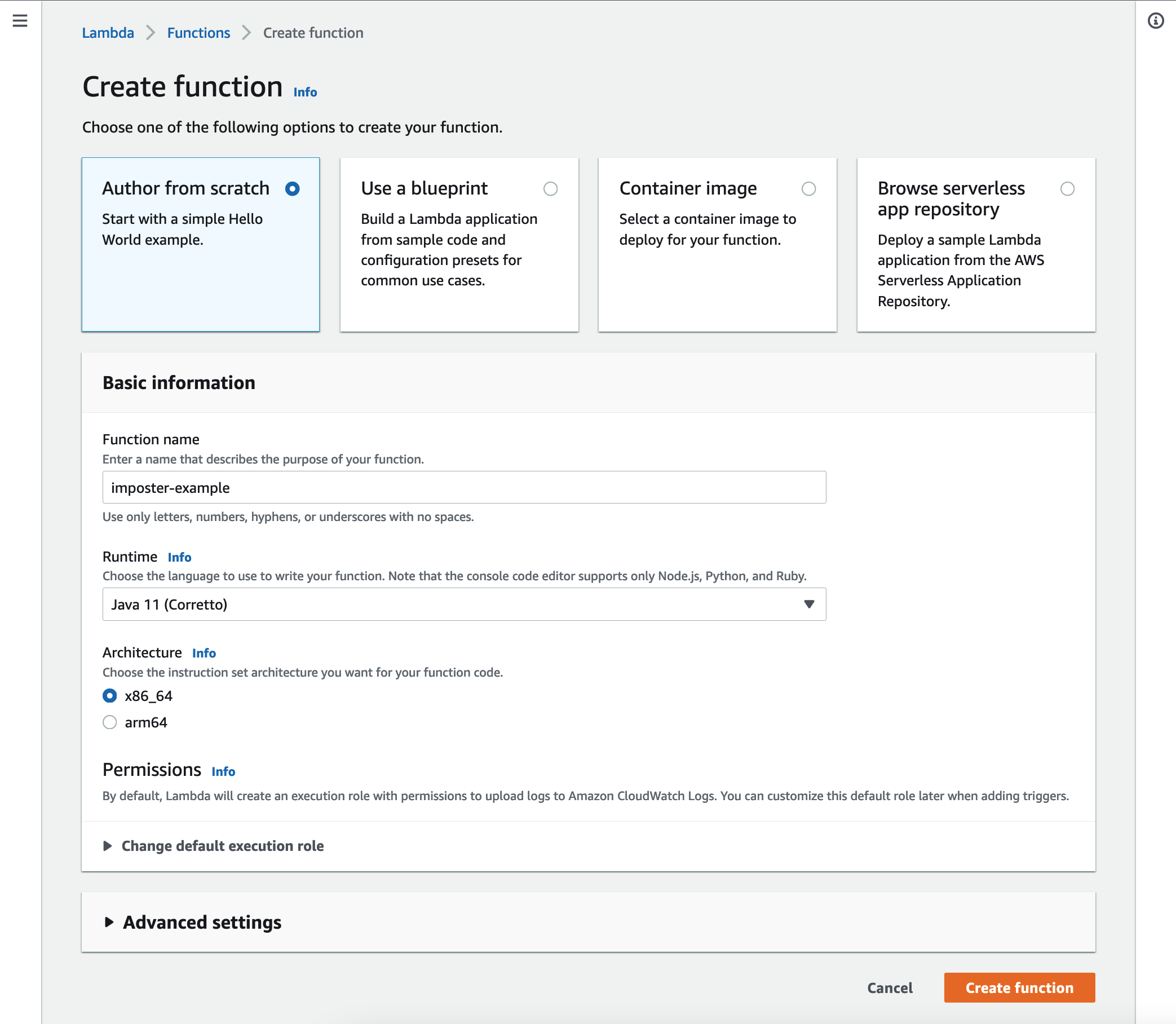
Step 2: Create your Lambda function
Open the AWS Lambda Console. Create a new function using the file you uploaded to S3 as the code source.
Important: Set the following:
- runtime:
Java 11 - architecture:
x86_64orarm64
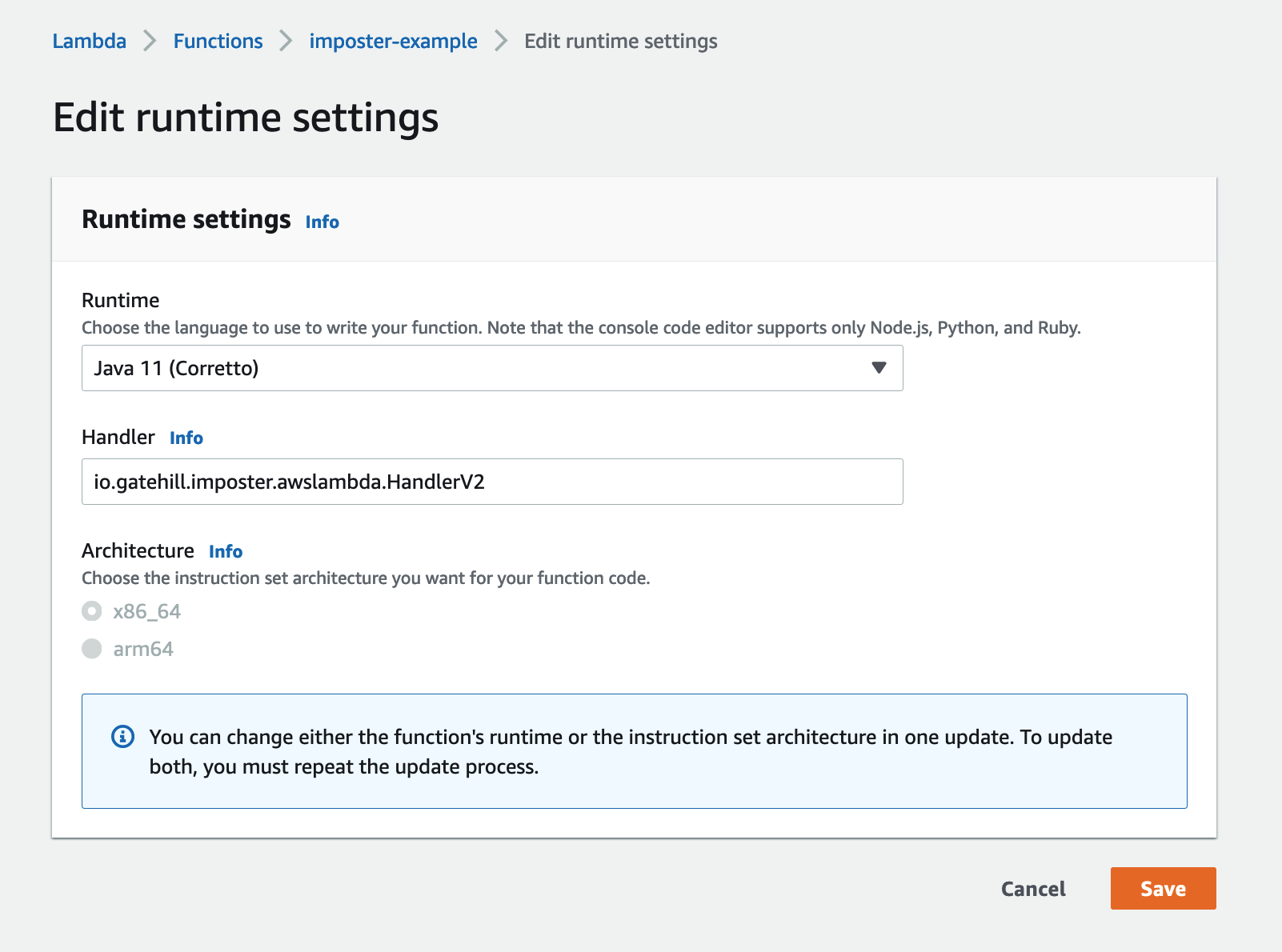
Step 3: Set handler
Under Runtime settings set the handler to: io.gatehill.imposter.awslambda.HandlerV2
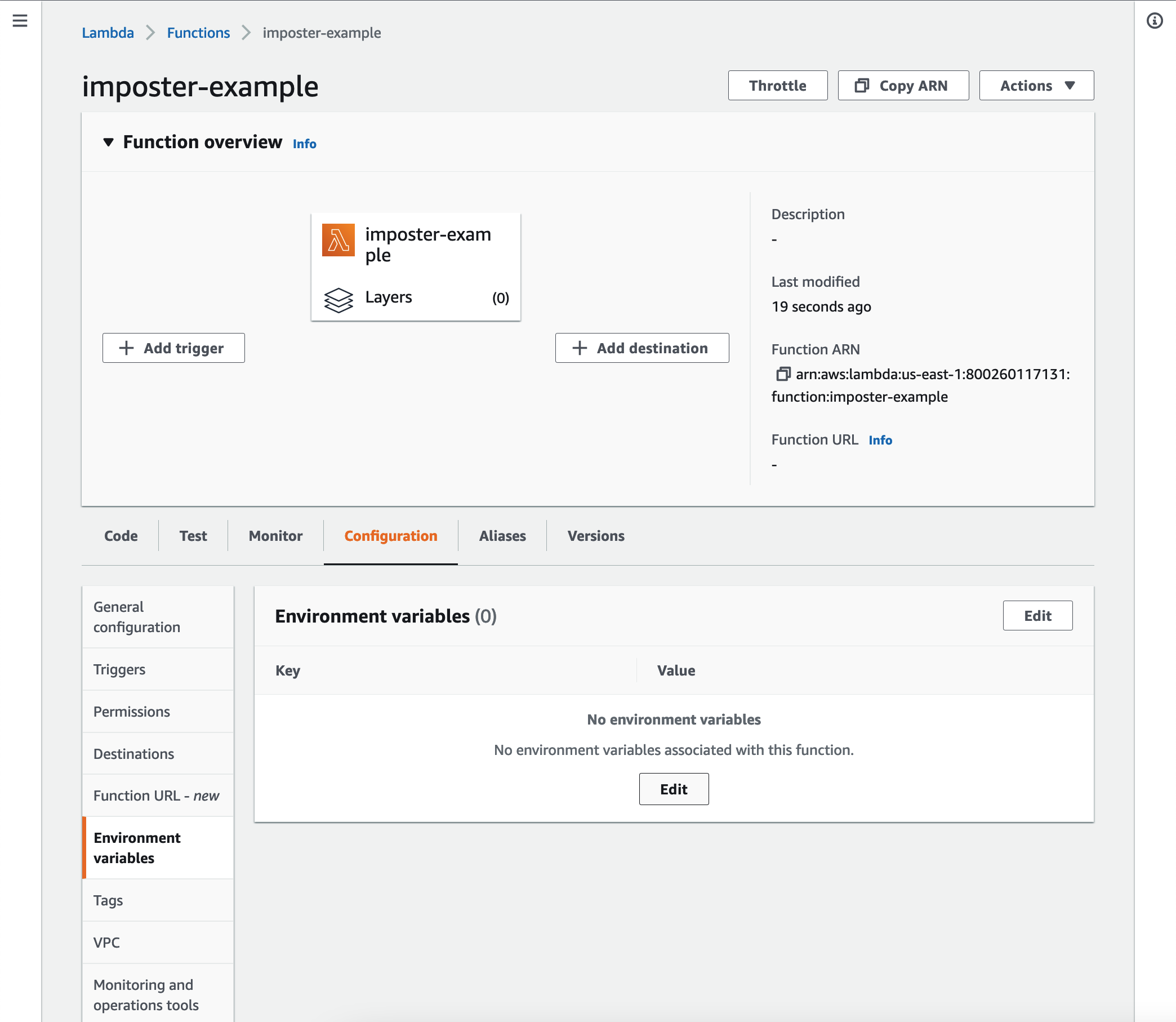
Step 4: Set environment variables
Under Configuration, add the following environment variable:
Set the environment variable to point to the path holding the configuration files:
Note: this is not the path to the YAML file - it is the directory ('prefix') under which the file exists in the bucket.
Important: Ensure the Lambda execution role has permission to access the S3 bucket containing your configuration.
See deploy/example/bucket-policy.json for an example IAM role.
Step 5: Enable function URL
Under Configuration, enable the 'Function URL' option - this will create an HTTPS endpoint for you to access Imposter.
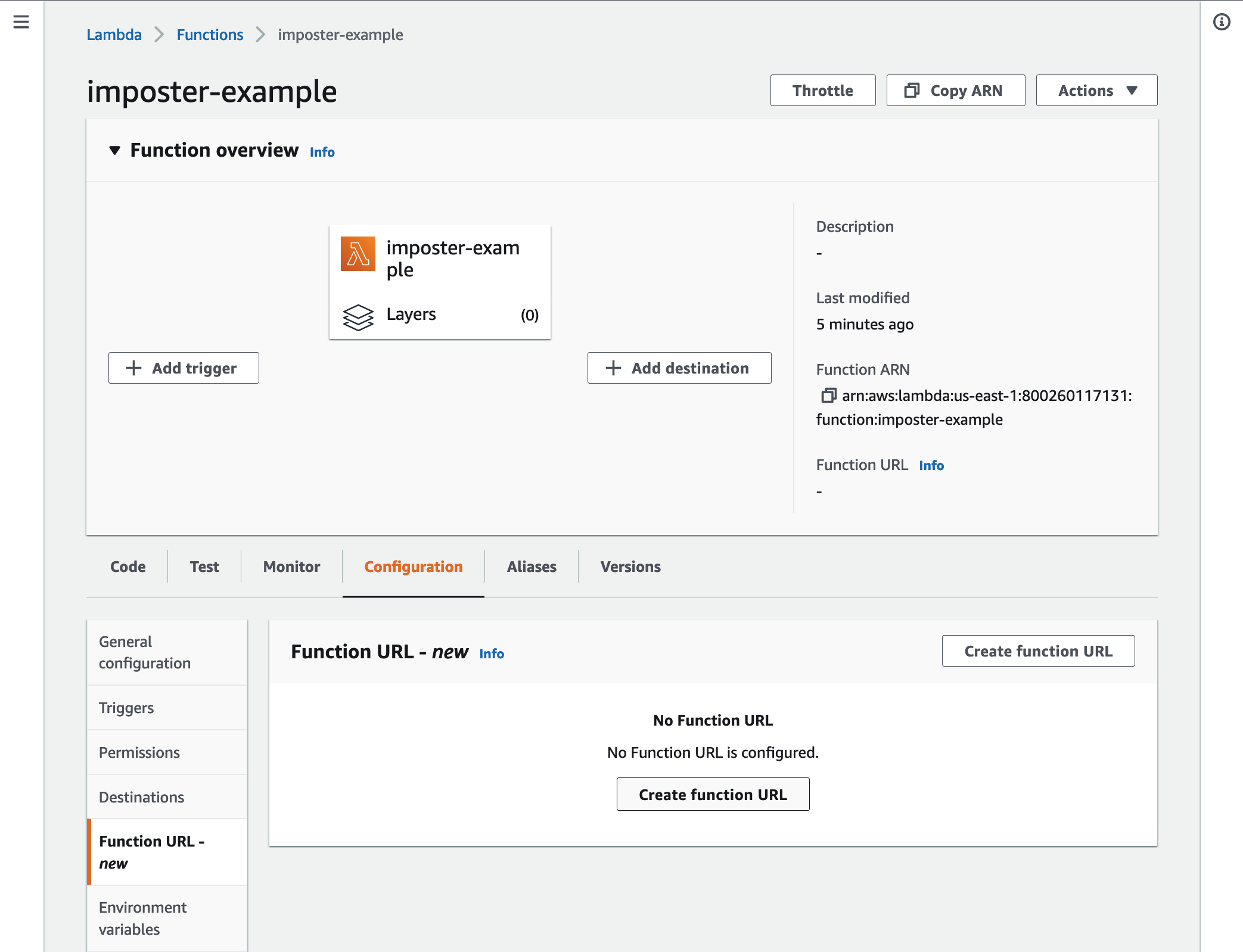
Once you have created it, you should see the Function URL:
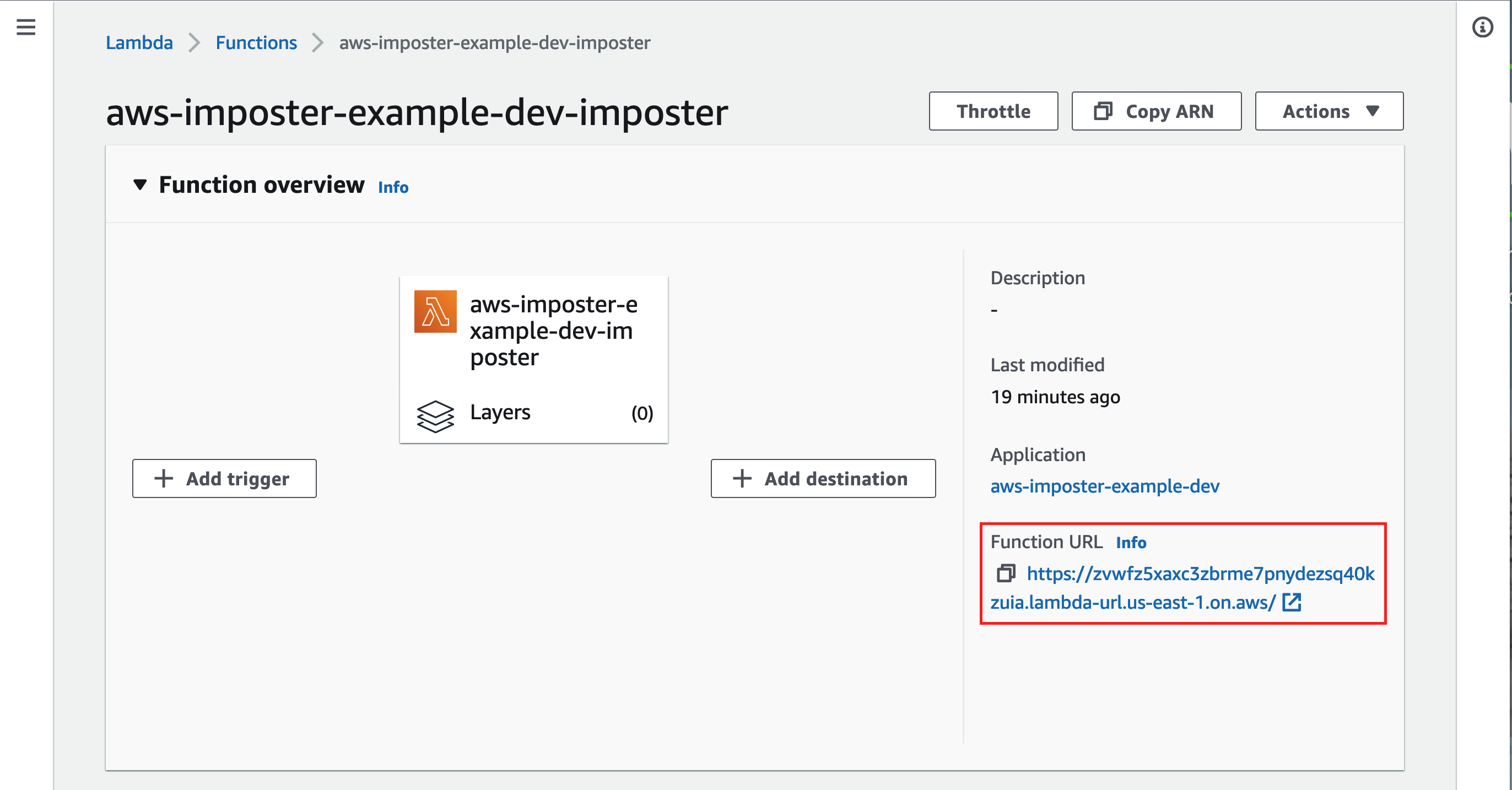
Step 6: Test the function
If all has gone well, you should be able to reach your Lambda function using the Function URL:
What's next
- Learn how to use Imposter with the Configuration guide.